Europe Floor Wage
Earning a living wage is a human right but garment workers in Europe struggle to make ends meet on their current wages. We developed a benchmark for living wages in European countries that reflects the reality of garment production in Europe.
Why focus on a Living Wage?
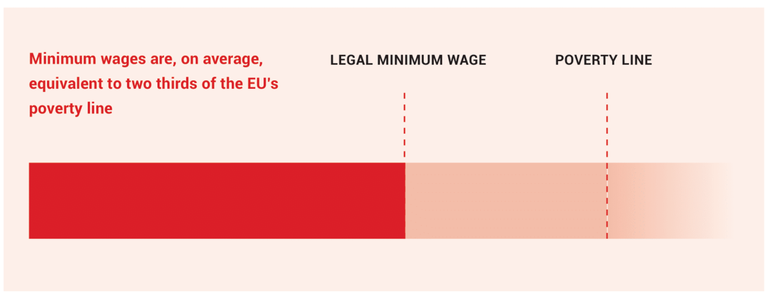
Buyers should pay the full price for the production of a garment. This includes a wage that the workers making the products can live on. Earning a living wage is a human right, but garment workers' wages in Europe are far below the poverty line.
In fact, the gap between current wages and a living wage is often bigger in European production countries than in Asian production countries. Brands take advantage of the fact that most people are unaware of this. Consumers are offered false assurances of fairer conditions when products are "made in Europe".

“There are times when we have nothing to eat.”
- Ukrainian garment worker
How much do workers need to live on?
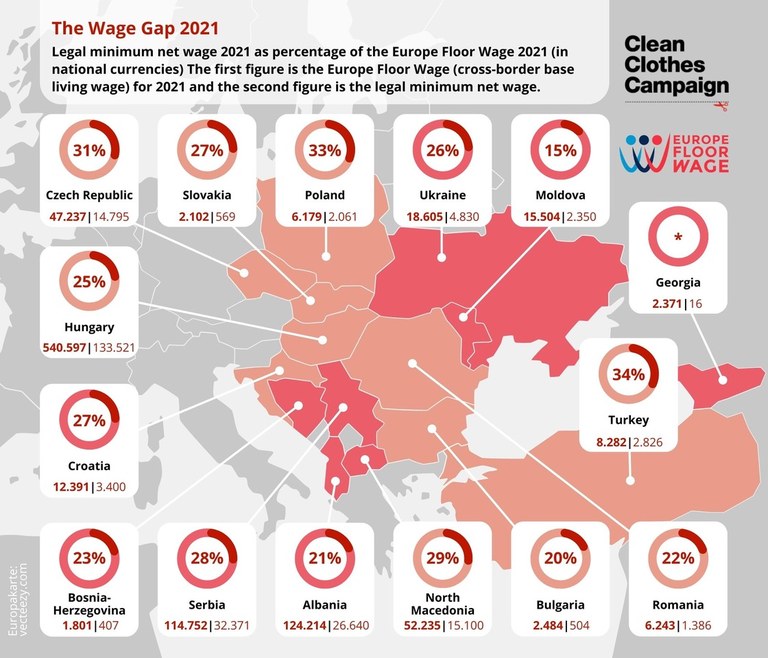
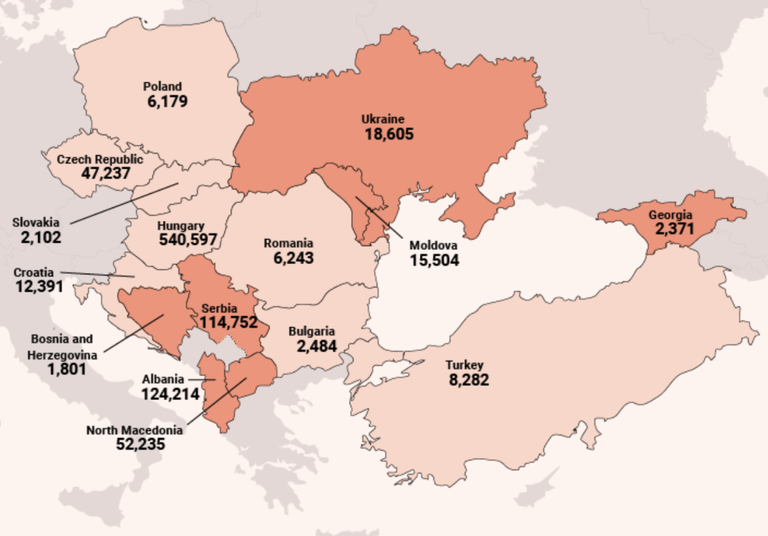
Living costs differ per country. We developed a cross-border benchmark for 15 European garment production countries. The infographic below shows what percentage of a living wage the legal minimum net wage pays per country. The first figure per country is the cross-border base living wage estimate, the second figure is the legal minimum net wage.
Visit FashionChecker.org to ask your favourite brands if they are paying workers a living wage.
Read more about our proposal for a living wage at WageForward.org



Why should a living wage be a regional concept?
In setting appropriate benchmarks for living wages in Europe, we seek to look beyond national borders. A concept that aims to put workers at its core has to take the global fast fashion business model into consideration. The power dynamics in global supply chains favour brands and retailers. While brands and retailers take the role of price setters, it is suppliers who must accept the prices offered to them.
Brands and retailers control how value is distributed along the supply chain, as well as where and when manufacturing will take place. The clothing industry therefore represents the quintessential example of a buyer-driven value chain. Because of the power that brands hold over their supplier through their purchasing practices, they have an extended responsibility to the workers of their suppliers. This is why brands and retailers are called principal employers.
The global fast fashion business model necessitates a policy that combats relocation competition between countries or regions. If it's cheaper to produce elsewhere, brands will move, and governments will keep legal wages low to incite brands to produce in their countries. With a cross-border approach, we are challenging the constant threat of relocation and preventing competition around wages.
With the Europe Floor Wage our goal is to put a floor on the 'race to the bottom' between and within European garment-producing countries. This does not mean that the Europe Floor Wage is the only possible estimate for a living wage. On the contrary: cross-border and national living wage benchmarks complement each other. This benchmark is an estimate which presents a base for negotiations and can be tailored by trade unions and labour NGOs in the work to achieve higher wages for workers in Central, East and Southeast Europe.
CCC urges the European Union to make a difference for workers through its minimum wage policy. In May 2020, CCC wrote a letter to the European Parliament's Committee for Employment and Social Affairs and the EU Commission welcoming their initiative “to ensure both that minimum wages are set at adequate and fair level and that workers have access to
minimum wage protection”.
Organisations behind the Europe Floor Wage

Eastern Europe's garment industry
-
April 18, 2023
Fast Fashion Purchasing Practices in the EU. Business relations between fashion brands and suppliers
This April 2023 report by today by the Fair Trade Advocacy Office (FTAO) and based on field research undertaken by Clean Clothes Campaign Europe demonstrates the existence of unfair trading practices in the European apparel industry. Based on interviews with suppliers, experts and trade union representatives in six EU member states – Bulgaria, Romania, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Italy and Germany – the report “Fast Fashion Purchasing Practices in the EU. Business relations between fashion brands and suppliers” paints a clear picture of the volatile, risky and unbalanced trade relations between brands and manufacturers.
-
September 13, 2022
Living Wage is Possible: Struggle for living wages in Croatia (2022)
The increased interest in the subject of living wage in Croatia came in mid-2021, a new method of calculating a living wage for Croatia was presented at the round table “Europe Floor Wage – a living wage is a human right”. The round table also marked the official start of the campaign for a living wage in Croatia. The Coalition for a Living Wage was launched, bringing together several civil society organisations - Pariter, the Centre for Peace Studies, the House of Human Rights, the Base for Workers’ Initiative and Democratization (BRID), Fashion Revolution Croatia, the Centre for Education Counselling and Research (CESI), then the Regional Industrial Union and the Independent Workers' Union of Croatia.
-
July 28, 2022
Europe Floor Wage Background paper 2022
The Europe Floor Wage is vital for the Clean Clothes Campaign’s strategy. Global fashion brands and retailers should – as principal employers – pay the full price to their suppliers, i.e. a price which includes a living wage instead of a poverty wage for garment workers. The reality is that the gap between the wages workers earn and a wage their families can live on is huge. This wage gap tends to be bigger in Europe than in Asia. In 15 European countries where garments are produced the gap is on average 1 : 4. Though the right to a living wage is a human right, workers’ actual wages are far below a living wage and in Central, East and South-Eastern Europe even fall considerably below the EU poverty line.
-
July 13, 2022
A LIVING WAGE IS A HUMAN RIGHT - A proposal for Italy, for the fashion industry and beyond
In this report we specifically address the issue of wages as the first, but not the only, urgent issue we need to act on in order to tackle the problem of in-work poverty and inequality in Italy, starting from the fashion supply chains. The concept of wage we are referring to is the floor living wage adopted by the Clean Clothes Campaign, which can be defined as the value of the net basic wage able to guarantee the worker and his/her family the satisfaction of basic needs and decent living conditions. The net basic pay is calculated without overtime bonuses, before incentives and allowances, and after taxes, taking into account only monetary disbursements.
1 - 4 of 15 Results
Country reports
-
-
-
-
-
-
January 23, 2020
Country profile Moldova (2019) - Romanian
This Romanian language country profile of Moldova sums up the state of the garment industry in the country in 2019.
-
January 23, 2020
Country profile Moldova (2019)
This country profile of Moldova sums up the state of the garment industry in the country in 2019.
1 - 7 of 25 Results